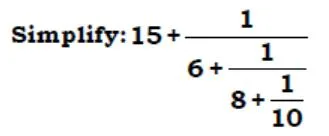solve ?
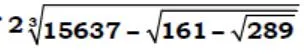
- 240
- 128
- 150
- 140
if x,y,z are natural numbers, then Find 2x + 3y -z = ?
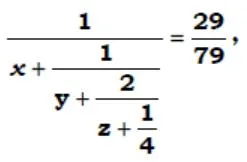
- 240
- 128
- 2
- 140
if a, b,c, are positive integers, then Find 4a+b+3c = ?
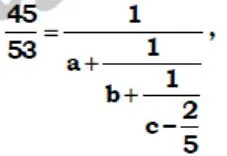
- 240
- 128
- 5
- 140
if a, b,c,d are integers, then Find a+b+c+d = ?
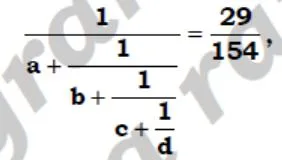
- 240
- 128
- 14
- 140
solve ?
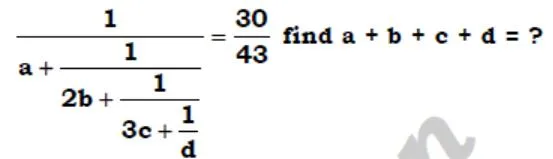
- 240
- 128
- 7
- 140
solve ?
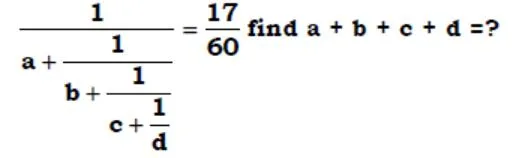
- 240
- 128
- 13
- 140
solve ?
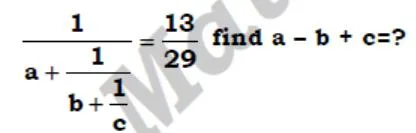
- 240
- 128
- 1
- 140
solve ?
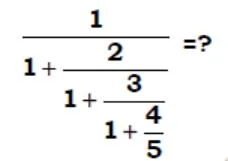
- 240
- 128
- 4/7
- 140
solve ?
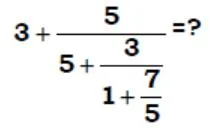
- 240
- 128
- 19/5
- 140
solve ?
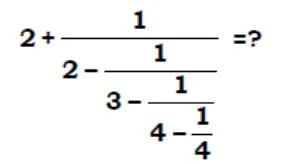
- 240
- 128
- 2(41/67)
- 140
- 240
- 128
- 15(81/492)
- 140
solve ?
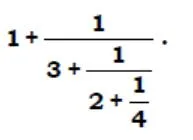
- 240
- 128
- 40/31
- 140
solve ?
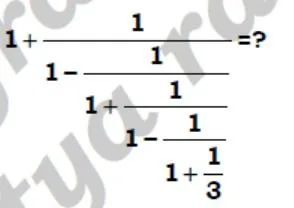
- 240
- 128
- 9/4
- 140
solve ?
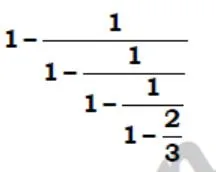
- 240
- 128
- 1/3
- 140
solve ?
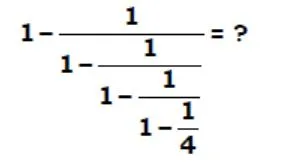
- 240
- 128
- 3/4
- 140
solve ?
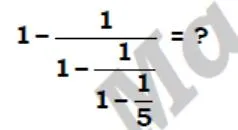
- 240
- 128
- 5
- 140
then Find 2x + 11⁄4
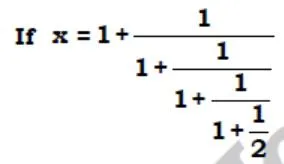
- 240
- 128
- 6
- 140
solve ?
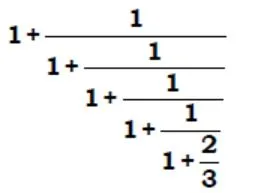
- 240
- 128
- 34/21
- 140
solve ?
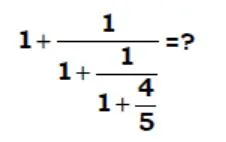
- 240
- 128
- 23/14
- 140
What does LTE stand for in 4G LTE?
- Long-Term Evolution
- Local Telecommunication Exchange
- Low-Tier Energy
- Landline Telephone Extension
Explanation:
- Long-Term Evolution (LTE) is the correct expansion, representing a standard for wireless broadband communication.
- Local Telecommunication Exchange is a fabricated term.
- Low-Tier Energy is unrelated to LTE.
- Landline Telephone Extension refers to traditional wired telephony.
Which organization developed the LTE standard?
- IEEE
- 3GPP
- ITU
- ISO
Explanation:
- 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) developed LTE as part of global telecommunication standards.
- IEEE focuses on general electronics and Wi-Fi standards.
- ITU regulates international telecom but did not design LTE.
- ISO deals with general standardization, not LTE specifically.
What is the theoretical maximum download speed of 4G LTE?
- 100 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
- 300 Mbps
- 10 Mbps
Explanation:
- 1 Gbps is the peak speed under ideal conditions (LTE-Advanced).
- 100 Mbps is common for standard LTE.
- 300 Mbps is achievable with carrier aggregation.
- 10 Mbps is typical for 3G networks.
Which technology does LTE use for data transmission?
- TDMA
- OFDMA
- CDMA
- FDMA
Explanation:
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) is used in LTE for downlink.
- TDMA (Time Division) was used in 2G.
- CDMA (Code Division) was used in 3G.
- FDMA (Frequency Division) is outdated for mobile broadband.
What is the minimum spectrum bandwidth required for LTE?
- 1.4 MHz
- 5 MHz
- 10 MHz
- 20 MHz
Explanation:
- 1.4 MHz is the smallest bandwidth LTE can operate on (though rarely used).
- 5 MHz is common for basic LTE.
- 10 MHz and 20 MHz offer higher speeds.
What is the primary advantage of LTE over 3G?
- Higher latency
- Lower data speeds
- Better spectral efficiency
- Limited mobility support
Explanation:
- Better spectral efficiency allows LTE to deliver higher speeds with less bandwidth.
- LTE has lower latency (~20-30 ms) than 3G (~100 ms).
- LTE supports speeds up to 1 Gbps, far exceeding 3G.
- LTE supports high mobility (e.g., high-speed trains).
Which Indian telecom operator first launched 4G LTE services?
- Airtel
- Jio
- Vodafone Idea
- BSNL
Explanation:
- Airtel launched India’s first 4G LTE service in Kolkata (2012).
- Jio launched later (2016) but popularized LTE with free data.
- Vodafone Idea and BSNL adopted LTE later.
What is MIMO in LTE?
- Multiple Input Multiple Output
- Mobile Internet Management Operation
- Multiplexed Interface Modulation Output
- Manual Input Manual Output
Explanation:
- Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) uses multiple antennas to improve speed and signal quality.
When is World Computer Literacy Day observed?
- September 16
- December 2
- October 24
- November 30
Explanation:
- December 2 – Established by NIIT in 2001 for its 20th anniversary
- Different from Software Freedom Day (September 16)
Which generation of cellular networks first introduced digital voice communication?
- 1G
- 2G
- 3G
- 4G
Explanation:
- 2G launched in early 1990s replaced analog 1G systems
- Introduced SMS and basic data services (GPRS/EDGE)
- Used GSM (Global System for Mobile) or CDMA standards
What is the typical range of Bluetooth technology?
- 50 meters
- 10 meters
- 100 meters
- 1 kilometer
Explanation:
- Class 2 Bluetooth (most common) has 10m range
- Operates in 2.4GHz band (2400-2483.5 MHz)
- Latest version Bluetooth 5.3 offers improved speed and range
Which wireless technology uses visible light for data transmission?
- Wi-Fi
- NFC
- Li-Fi
- RFID
Explanation:
- Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) uses LED bulbs for data transfer
- Can achieve speeds up to 224 Gbps in lab conditions
- More secure than radio-based technologies as light doesn’t penetrate walls
What does MTSO stand for in cellular networks?
- Mobile Telephone Service Operator
- Mobile Tower Switching Office
- Main Telecommunication Switching Office
- Multiple Tower Service Operator
Explanation:
- MTSO connects all cell towers in an area via fiber optics
- Stores SIM card data and manages handoffs between cells
- Links cellular network to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)
Which frequency bands does Wi-Fi primarily use?
- 900 MHz and 1.8 GHz
- 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- 3.7 GHz and 6 GHz
- 10 GHz and 12 GHz
Explanation:
- 2.4GHz (longer range but more crowded)
- 5GHz (faster speeds, less interference)
- Wi-Fi 6E adds 6GHz band for even better performance
What is the maximum speed of 1G networks?
- 1 Kbps
- 2.4 Kbps
- 10 Kbps
- 64 Kbps
Explanation:
- 1G (1980s) was analog with very limited capacity
- Only supported voice calls with poor quality
- Used AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) technology
Which technology is used for contactless payments like Apple Pay?
- Bluetooth
- Li-Fi
- NFC
- SATCOM
Explanation:
- NFC (Near Field Communication) works within 4cm range
- Operates at 13.56 MHz frequency
- Used in mobile payments, transit cards, and device pairing
What does RAN stand for in 5G networks?
- Radio Access Node
- Radio Access Network
- Remote Area Network
- Random Access Number
Explanation:
- RAN connects devices to the core network via radio signals
- In 5G includes small cells, macro cells and massive MIMO antennas
- Key for achieving 5G’s low latency (1ms target)
Which cellular generation first enabled video calling?
- 2G
- 3G
- 4G
- 5G
Explanation:
- 3G (2000s) provided sufficient bandwidth (2Mbps+)
- Used UMTS/WCDMA technology
- Also enabled mobile TV and proper web browsing
What is the primary purpose of a SIM card?
- Device storage
- Subscriber identification
- Battery management
- Display control
Explanation:
- SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) authenticates users
- Contains IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity)
- Modern eSIMs are embedded directly in devices
Which Wi-Fi security protocol is considered most secure today?
- WEP
- WPA
- WPA3
- WPS
Explanation:
- WPA3 (2018) uses 192-bit encryption (vs WPA2’s 128-bit)
- Protects against offline dictionary attacks
- Mandatory for Wi-Fi 6 certified devices
What is the main advantage of 5G over 4G?
- Larger phone batteries
- Lower latency
- Better voice quality
- Cheaper infrastructure
Explanation:
- 5G latency as low as 1ms (vs 4G’s 30-50ms)
- Enables real-time applications like remote surgery
- Also offers higher speeds (up to 20Gbps) and more capacity
What does SSID refer to in Wi-Fi networks?
- Security Standard ID
- Signal Strength Indicator
- Network name
- Router model number
Explanation:
- SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the visible network name
- Maximum 32 characters long
- Broadcast can be disabled for “hidden networks”
Which technology has the longest operational range?
- NFC
- Bluetooth
- SATCOM
- Li-Fi
Explanation:
- SATCOM (Satellite Communications) works globally
- Geostationary satellites orbit at 35,786 km altitude
- Used in maritime, aviation, and remote area communications
Which wireless technology is used in inventory tracking?
- Li-Fi
- RFID
- NFC
- Bluetooth
Explanation:
- RFID tags can be passive (no battery) with range up to 10m
- Used in supply chain, retail, and access control systems
- Operates at various frequencies (LF, HF, UHF)
Which cellular technology introduced OFDMA modulation?
- 2G
- 3G
- 4G LTE
- 5G
Explanation:
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)
- Fundamental to LTE’s efficiency and speed
- Allows multiple users to share same frequency channel
What is the main difference between Wi-Fi and cellular networks?
- Wi-Fi is always faster
- Cellular doesn’t need devices
- Licensed vs unlicensed spectrum
- Wi-Fi can’t transmit data
Explanation:
- Cellular uses licensed spectrum (controlled by carriers)
- Wi-Fi uses unlicensed spectrum (free but crowded)
- Cellular offers mobility, Wi-Fi typically better for stationary use
Which technology enables international mobile usage?
- Li-Fi
- Roaming agreements
- NFC
- WPA3
Explanation:
- Roaming allows use of partner networks abroad
- Enabled by GSMA standards and carrier agreements
- May incur additional charges for voice/data usage
What is the key advantage of massive MIMO in 5G?
- Smaller phones
- Increased capacity
- Cheaper plans
- Longer battery life
Explanation:
- Massive MIMO uses dozens of antennas (64T64R common)
- Focuses signals directionally (beamforming)
- Can serve many users simultaneously in same frequency
What is the primary use of CDMA in cellular networks?
- Battery saving
- Multiple access
- Display control
- Voice encryption
Explanation:
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) allows many users to share same frequency
- Each call uses unique code
- Alternative to GSM’s TDMA approach in 2G/3G
Which technology enables satellite phones?
- Li-Fi
- NFC
- SATCOM
- WPA3
Explanation:
- SATCOM systems like Iridium, Globalstar provide global coverage
- Use LEO (Low Earth Orbit) or GEO (Geostationary) satellites
- Essential for maritime, aviation and remote area communications